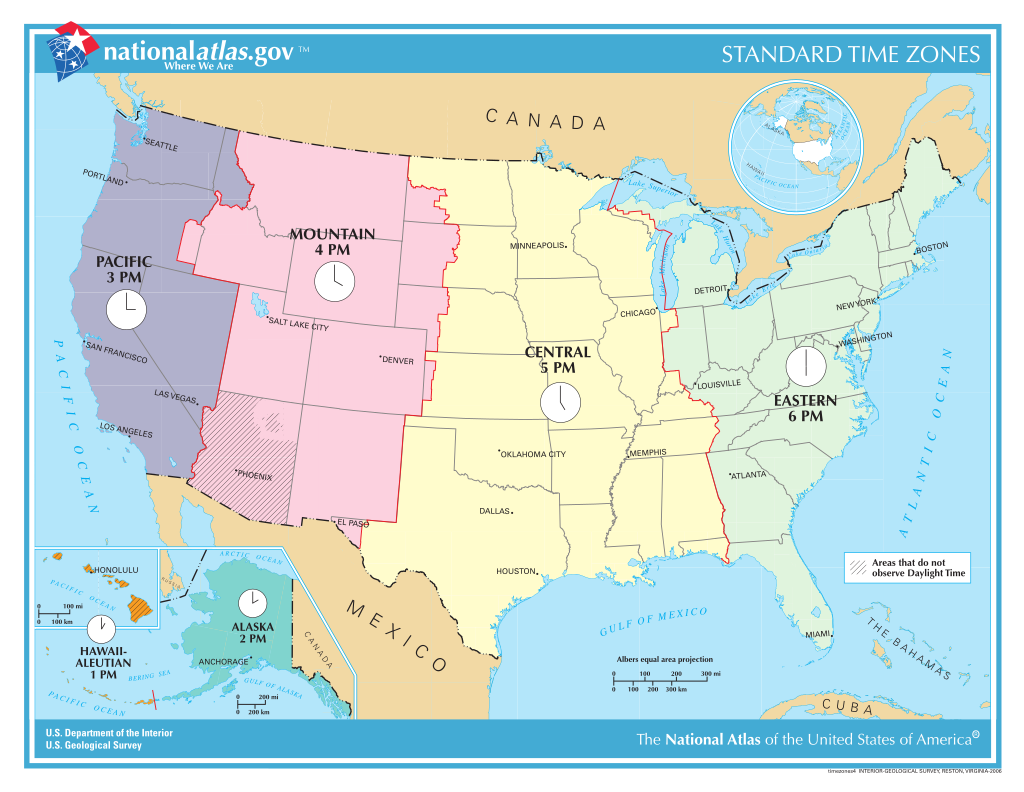
USA Time Zones ~ The United States, due to its vast geographical expanse, spans multiple time zones, each playing a crucial role in synchronizing activities across the country. From the Atlantic to the Pacific, and even extending to Hawaii and Alaska, these time zones help manage the differences in local time across the states. This article provides an overview of the time zones in the U.S., including their significance and the regions they cover.
The Six Primary U.S. Time Zones
1. Eastern Standard Time (EST)
– Offset: UTC -5 hours (Standard Time), UTC -4 hours (Daylight Saving Time, EDT)
– Coverage: The Eastern Time Zone is the most populous time zone in the United States. It includes major cities like New York, Washington D.C., Atlanta, and Miami. The states fully or partially in this zone include New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Georgia, and Florida, among others. The Eastern Time Zone is crucial as it is home to the nation’s capital and many of its major financial centers, including Wall Street.
2. Central Standard Time (CST)
– Offset: UTC -6 hours (Standard Time), UTC -5 hours (Daylight Saving Time, CDT)
– Coverage: The Central Time Zone covers a large portion of the U.S., including cities like Chicago, Dallas, Houston, and New Orleans. States fully or partially in this zone include Illinois, Texas, Minnesota, and Missouri. The Central Time Zone is important for agriculture, manufacturing, and energy industries, especially in the Midwest and southern parts of the country.
3. Mountain Standard Time (MST)
– Offset: UTC -7 hours (Standard Time), UTC -6 hours (Daylight Saving Time, MDT)
– Coverage: The Mountain Time Zone encompasses states such as Colorado, Arizona, Utah, and New Mexico. Cities like Denver, Phoenix, and Salt Lake City are in this zone. Arizona is unique in that it does not observe Daylight Saving Time, except for the Navajo Nation, which does. The Mountain Time Zone covers a region known for its national parks, mountains, and deserts.
4. Pacific Standard Time (PST)
– Offset: UTC -8 hours (Standard Time), UTC -7 hours (Daylight Saving Time, PDT)
– Coverage: The Pacific Time Zone includes the states along the West Coast, such as California, Washington, and Oregon. Major cities like Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, and Portland fall within this zone. The Pacific Time Zone is vital for the entertainment industry, technology sector, and international trade, given its proximity to Asia.
5. Alaska Standard Time (AKST)
– Offset: UTC -9 hours (Standard Time), UTC -8 hours (Daylight Saving Time, AKDT)
– Coverage: Alaska, the largest state by area, is in its own time zone, known as Alaska Standard Time. The zone covers most of the state, including Anchorage and Juneau. Alaska’s unique position far to the north and west means that its daylight hours can vary dramatically with the seasons, from nearly 24 hours of daylight in summer to only a few hours in winter.
USA Time Zones
6. Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time (HST)
– Offset: UTC -10 hours (No Daylight Saving Time)
– Coverage: The Hawaii-Aleutian Time Zone covers the Hawaiian Islands and the westernmost part of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. Unlike most other U.S. time zones, Hawaii does not observe Daylight Saving Time, which means its time remains constant throughout the year. Honolulu, the state’s capital, is a major city within this time zone.
Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Daylight Saving Time is observed in most parts of the United States, where clocks are set forward by one hour during the summer months to make better use of daylight in the evening. DST typically begins on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first Sunday in November. However, some regions, such as most of Arizona and Hawaii, do not observe Daylight Saving Time, maintaining their standard time throughout the year.
The Role of Time Zones in Daily Life
Time zones in the U.S. are not just about geography; they influence everything from business operations to broadcast schedules, transportation, and even social interactions. For instance, financial markets in New York open at 9:30 AM Eastern Time, which means it’s 6:30 AM in Los Angeles. This difference affects how businesses operate and coordinate across the country. Similarly, television networks adjust their programming to ensure that shows air at convenient times in each time zone.
Time Zone Boundaries and Exceptions
While the primary time zones generally follow state lines, there are several exceptions where time zones split states or even cities. For example, Indiana and Kentucky are divided between the Eastern and Central Time Zones. The time zone boundaries are set by the U.S. Department of Transportation and are periodically reviewed to reflect changes in population, commerce, and transportation patterns.
Understanding the time zones of the United States is essential for coordinating activities across the country, from business meetings to travel plans. The time zones reflect the vastness and diversity of the nation, ensuring that each region operates efficiently within its own local time. Whether planning a cross-country trip, scheduling a virtual meeting, or simply watching your favorite TV show, being aware of the time zones and how they interact is key to staying on track in today’s interconnected world.
USA Time Zones